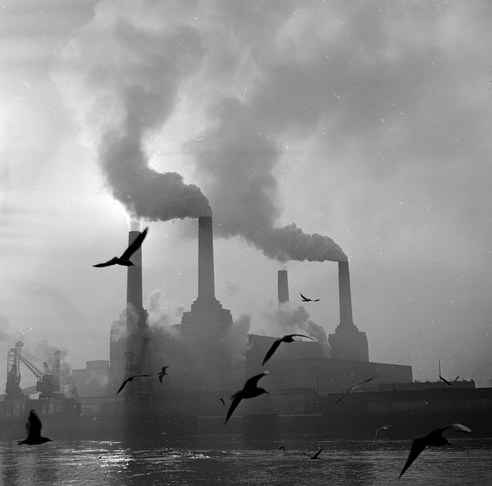
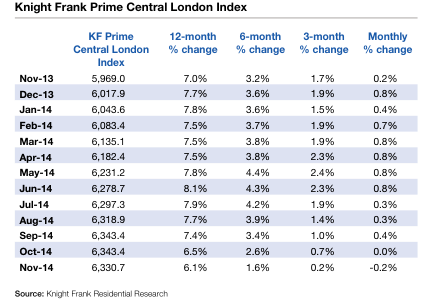
After a big spike in reporters’ attention following Apple’s decision to move its headquarters into the grade 2 star listed art deco Building, Battersea Power Station has gone quieter in mainstream media over the last months. This doesn’t mean that nothing has changed and Spectacle has been following the latest initiatives of Battersea Power Station Development Company around the beloved building designed by Giles Gilbert Scott. Unfortunately much of the news is not reassuring.
Bad news or good news? Bad and good, as usual, are mixed up in the opacity of corporate communication, where everything can be spun according to the most convenient narrative. In fact, the general public is probably aware that the biggest and richest company in the world, Apple, have expressed their intention to move into the refurbished power plant. Apple has been welcomed almost unanimously in mainstream media (among others: BBC, The Guardian, Evening Standard) as good news. Meanwhile only Spectacle’s blog reported that the East Wall has been completely demolished in order to make windows and give light to Apple’s offices.
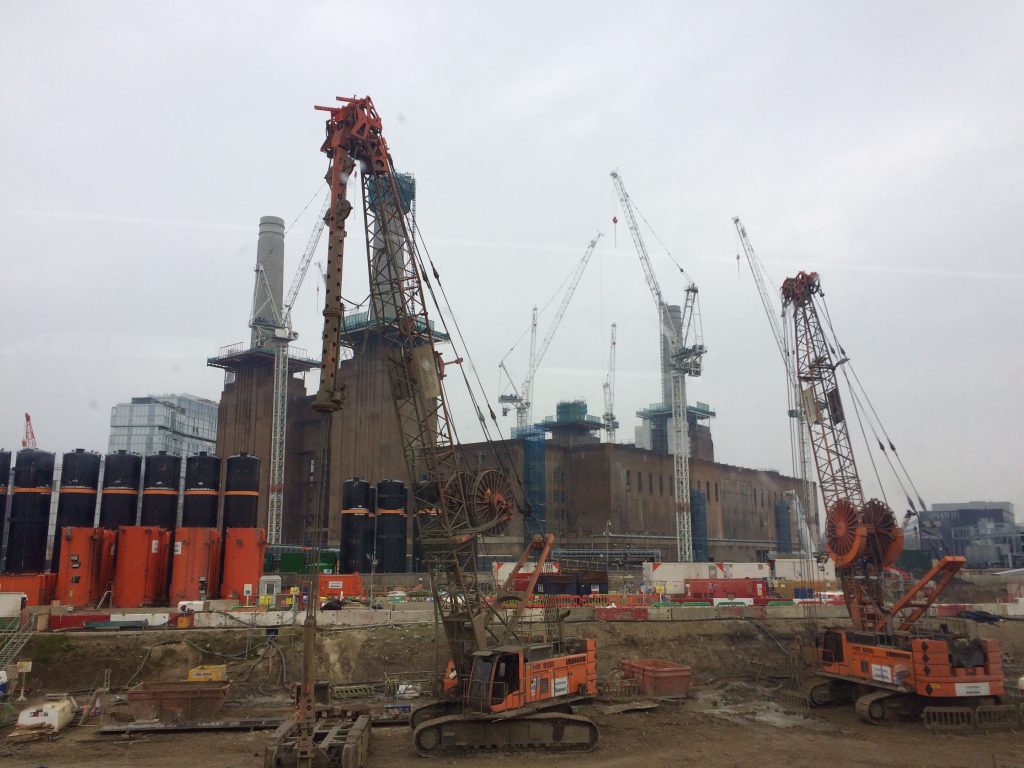

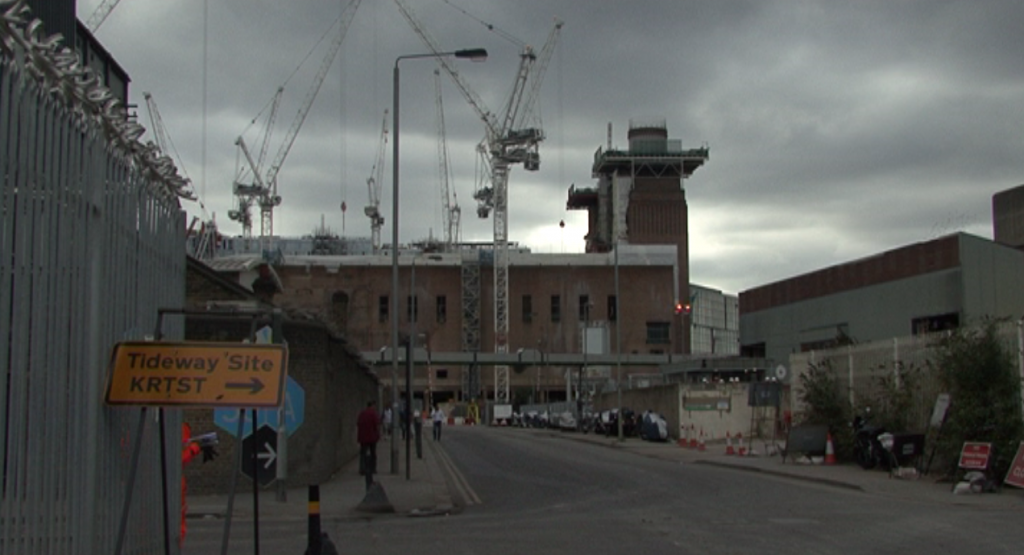
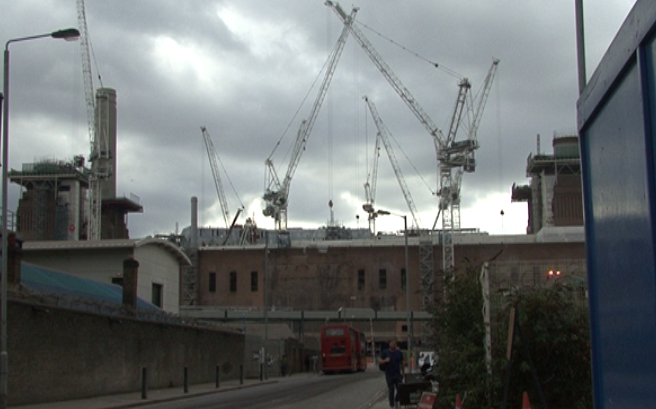
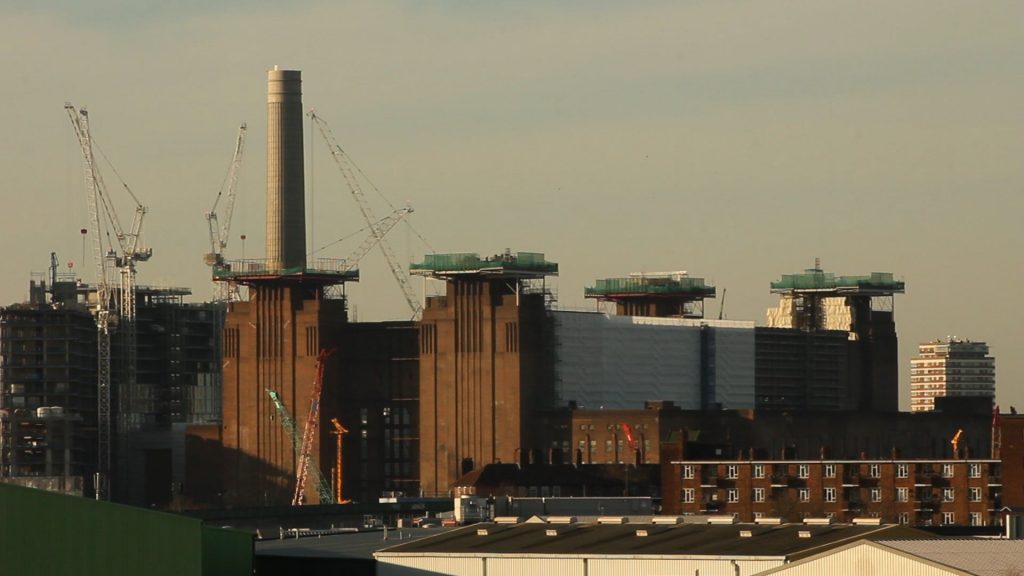
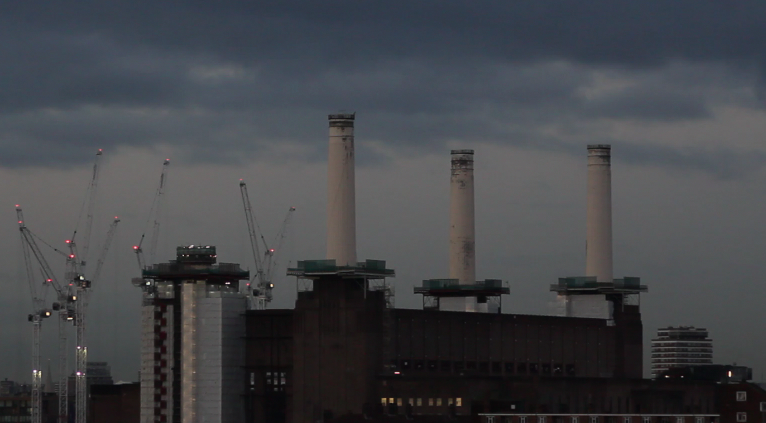
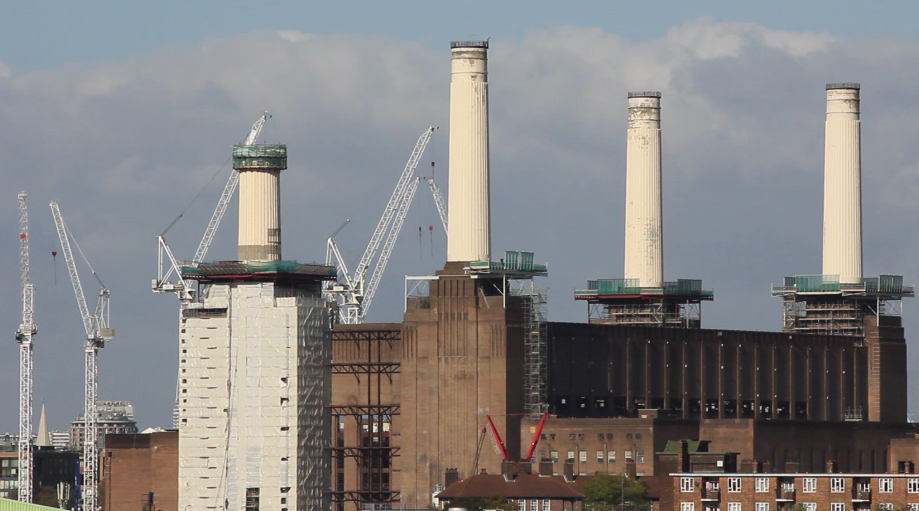
Battersea Power Station – three of the four chimneys have been rebuilt. (Spectacle, 10/03/17)
This major loss, unreported in the mainstream media, follows a curious ’destroy-to-preserve’ strategy repeatedly applied to portions of the Battersea Power Station. Even though best practice in heritage interventions recommends to keep existing structures, the iconic chimneys have gone and been replaced with replicas. In our opinion this is the most evident distortion produced by developer-led preservation, as shown in our film Battersea Power Station: Selling an Icon.
The demolitions (east wall and chimneys) have been approved by all regulatory agencies (Historic England – former English Heritage – and Wandsworth Council) and justified with the greater good of bringing the Battersea Power Station back to life. But what good has the 9 billion development – one of the biggest in Europe – delivered so far? The works to rebuild the chimneys have proceeded and, at the moment, three newly built chimneys stick out the spoiled art deco power station. Hopefully Londoners will be able to once again admire the four chimneys back on the Battersea skyline, even though they are fakes. Better than nothing? Maybe.
PUBLIC NOT PUBLIC
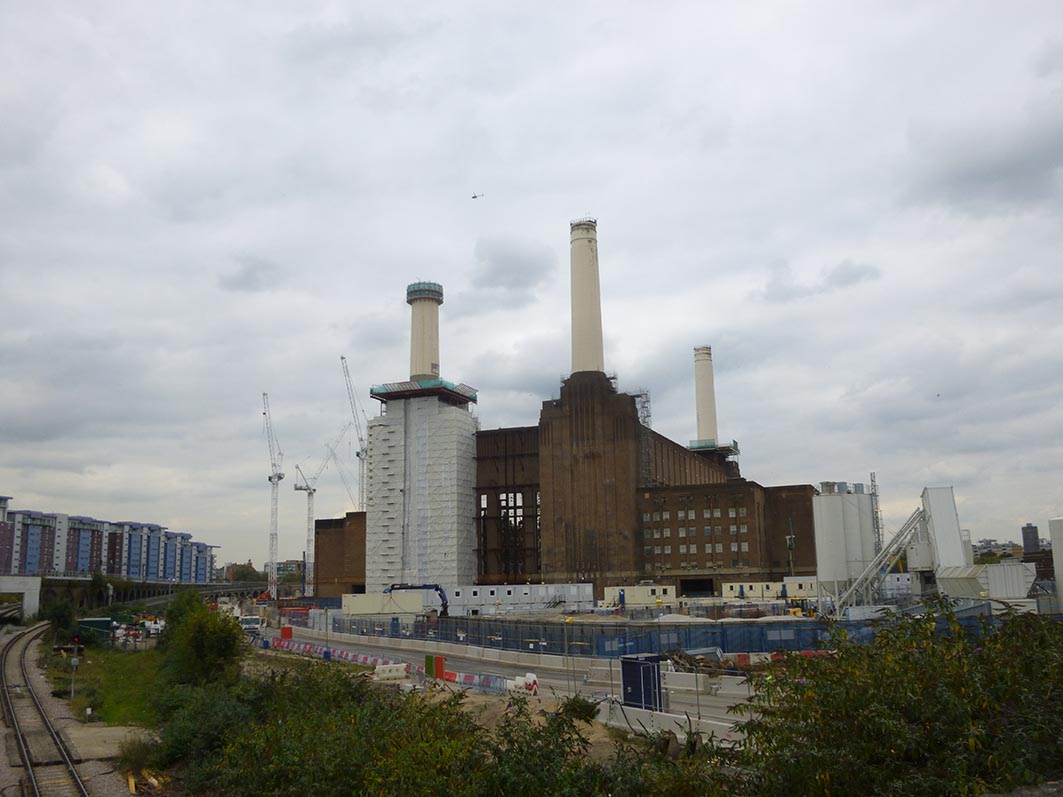
Battersea Power Station Development Company, through it’s Chief Executive Rob Tincknell, have recently announced the opening of a riverside walk in the development area: “We are delighted that we are able to open new public spaces for London and are starting to bring the power station and its surrounds back into London life” (Reported on the Evening Standard). Despite the enthusiasm in the wording, the ‘public space’ Rob Tincknell is talking about is a private walk squeezed between the river and Phase 1 of the development. This promenade is going to be integrated into the wider riverside walk that will be opened in front of the Power Station. Like the rest of the development, this space is private and merely open to public, which is quite different from being ‘public space’.
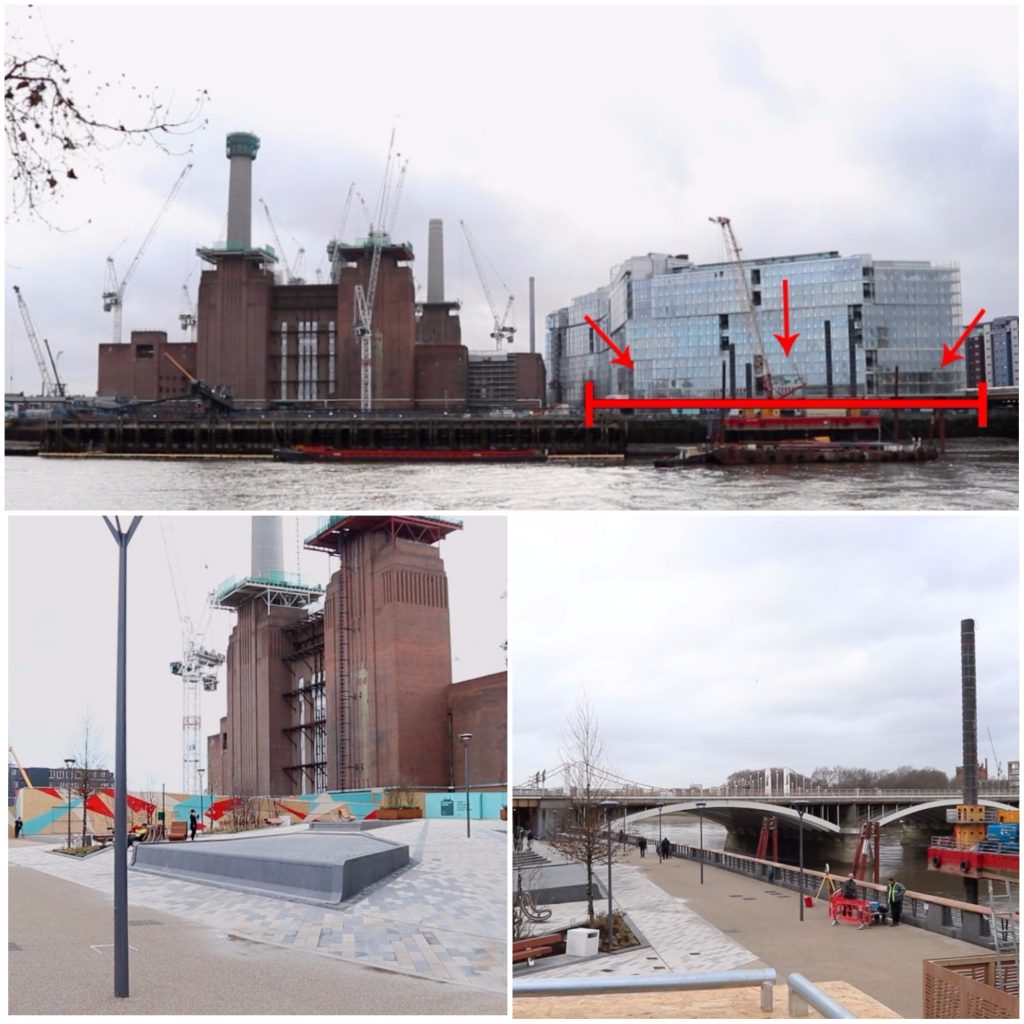

The recently open riverside promenade (Spectacle, 04/03/2015)
While filming the new Riverside promenade, our naive crew, believing in the “public space” hype outlined by the developers, acted as if it was a real public area. Unfortunately we have been brought back to reality when the local security reminded us that the landlord decided that smoking was not allowed on the site. Thanks to this sensible management, our health has been preserved. Nevertheless it seems unlikely that a privately policed space will guarantee free enjoyment of the river. If they were to outlaw picnics (maybe to help food shops in the development) or a protest, there would be little room for complaint: that’s what you get when you privatise public spaces.
The Guardian in the past has warned about the effects already produced by this public/private mix on the shores of the River Thames, that became a “bafflingly complex labyrinth of private obstructions and municipal confusion – and a struggle over land rights that could have serious consequences for common access to the river”. Not a great prelude to what developers offer as a unique experience.
PLANNING NOT PLANNING
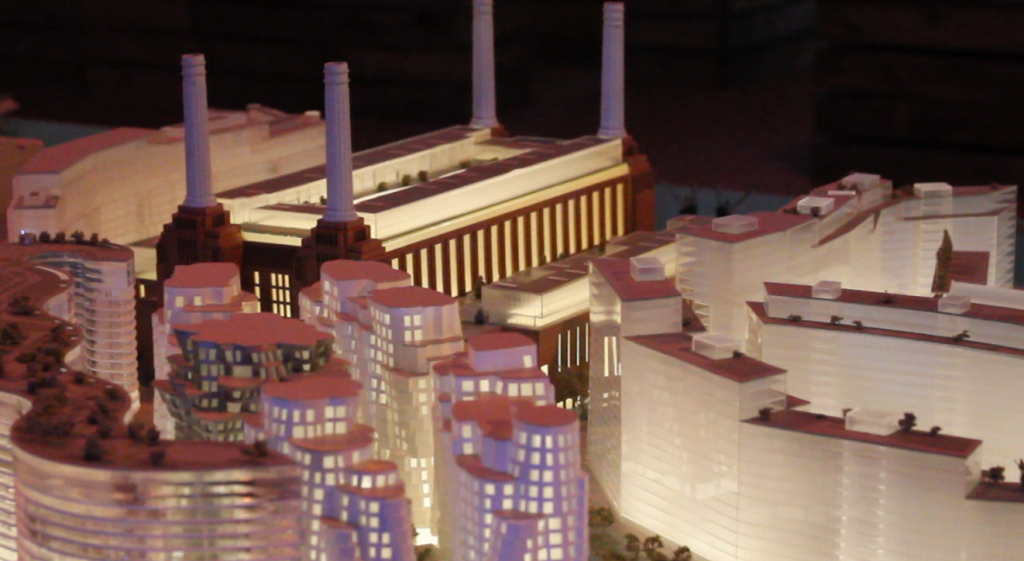
The pretentious 230 pages long ‘manifesto’ on Place Making put forward by the Battersea Power Station Development Company gives paramount importance to mixed use and mixed tenancy. Despite the commitment to deliver housing (and some affordable housing) to London’s population, the Malaysian consortium that leads the development has changed its mind, switching from luxury flats to offices.

Cover page of Battersea Power Station Development Company book on ‘place making’ (2014)
Battersea Power Station Development Company have put forward an application for a change of use for Phase 3 of the project. Developers are seeking to turn two buildings, by starchitects Frank Gehry and Norman Foster, – whose flats have already been displayed for sale – from residential to office use. The Financial Times, reported the proposed change is due to a drastic drop in the prime housing market price, whereas demand for office space seems to be holding a higher value. Rob Tincknell in the Financial Times had to justify the plan: “The great thing about a long-term scheme like this is we can adjust with the markets. If there’s no residential market and a very strong office market then we will build offices”.
The same Tincknell that now praises flexibility, in the past gave an interview to Peter Watts, for his book “Up in Smoke” about the history of Battersea Power Station, making clear how Battersea Power Station Development Company came up with their surefire recipe to make Battersea the perfect place: “57% residential. Of the remaining 43% that’s about 3.4m sq ft, 1.2m retail and restaurants, 1.7m sq ft of offices and the balance in hotels, leisure and community space.” We wonder what happened to the pseudo-scientific plan for mixing uses and people in the “new place”, allegedly the result of a long consultation with local people. Maybe it wasn’t that important, since Tincknell tells the Financial Times now that “I could easily see us adding another million square feet (of office space)” and taking out a hotel and lots of residential from the scheme.
Battersea Power Station Community Group, virtually the only critical voice in the neighbourhood whose opinion has never been taken into account by the developers, have stood against the proposed plan: “The Gehry and Foster blocks should become social, affordable and mid-priced housing. There could be some office space at the lower levels. But with a housing crisis in London of unprecedented severity, these buildings should not be given over to offices in their entirety”.
Keep following our blog for updates and other contradictions produced by the big bang development of Battersea Power Station
Watch more videos on Battersea Power Station
Click Battersea Power Station for more blogs
See our Battersea Power Station project pages for more information and videos.
Spectacle homepage Like Spectacle Documentaries on Facebook
Follow SpectacleMedia on Twitter